LEVERAGING MACHINE LEARNING METHODS IN PREDICTING AND ANALYZING THE ASSOCIATION BETWEEN DIETARY INFLAMMATORY INDEX AND ALOPECIA
Abstract
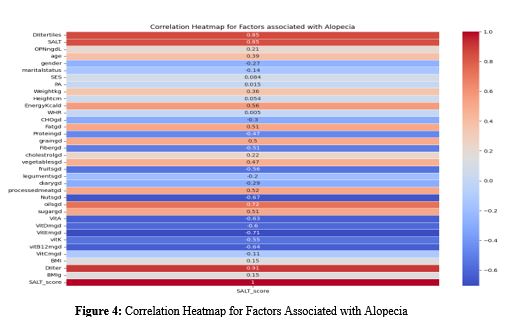
Alopecia areata (AA) is considered a chronic inflammatory disorder and represents a worldwide public health problem. Diet was hypothesized to play a role in AA development, but little is known about the association between the dietary inflammatory index (DII) and AA. This study aimed to analyze the correlation between AA and DII using machine learning at aj(ML) models. DII scores were ascertained using a food frequency questionnaire (FFQ), and the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score was used to classify the severity of AA. Three machine learning models were developed: K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) with dimensionality reduction to prevent overfitting, Logistic Regression with L2 regularization, and Random Forest enhanced through grid search for hyperparameter tuning. Additionally, to further understand the association between DII and AA, partial dependence plots (PDPs), correlation analysis, and multiple evaluation indicators, including accuracy, F1 score, recall, precision, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC AUC) were used. Surprisingly, higher DII scores are significantly associated with an increase in AA. In addition, a higher inflammatory diet was associated with increased severity of the disease. The highest accuracy was achieved by the Random Forest Classifier 98.77%, whereas 98.64% and 98.10% were achieved by Logistic Regression and KNN models, respectively. This study presents evidence about the association between inflammatory food patterns and AA, which may provide important implications for future treatment and dietary interventions. A high score on the DII indicated an increased proinflammatory potential of food intake and was associated with an increase in AA
Full text article
References
Abu Alfeilat, H. A., Hassanat, A. B., Lasassmeh, O., Tarawneh, A. S., Alhasanat, M. B., Eyal Salman, H. S., & Prasath, V. S. (2019). Effects of distance measure choice on k-nearest neighbor classifier performance: a review. Big data, 7(4), 221-248. DOI: 10.1089/big.2018.0175
Ahammed, M., Al Mamun, M., & Uddin, M. S. (2022). A machine learning approach for skin disease detection and classification using image segmentation. Healthcare Analytics, 2, 100122. DOI: 10.1016/j.health.2022.100122
Alanazi, R. (2022). Identification and prediction of chronic diseases using machine learning approach. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2022(1), 2826127. DOI: 10.1155/2022/2826127
Anand, V., Gupta, S., Nayak, S. R., Koundal, D., Prakash, D., & Verma, K. D. (2022). An automated deep learning models for classification of skin disease using Dermoscopy images: A comprehensive study. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 81(26), 37379-37401. DOI: 10.1007/s11042-021-11628-y
Azadbakht, L., & Esmaillzadeh, A. (2009). Red meat intake is associated with metabolic syndrome and the plasma C-reactive protein concentration in women. The Journal of nutrition, 139(2), 335-339. DOI: 10.3945/jn.108.096297
Bagheri, S., Zolghadri, S., & Stanek, A. (2022). Beneficial effects of anti-inflammatory diet in modulating gut microbiota and controlling obesity. Nutrients, 14(19), 3985. 10.3390/nu14193985
Bosma-den Boer, M. M., van Wetten, M. L., & Pruimboom, L. (2012). Chronic inflammatory diseases are stimulated by current lifestyle: how diet, stress levels and medication prevent our body from recovering. Nutrition & metabolism, 9, 1-14. DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-32
Buitinck, L., Louppe, G., Blondel, M., Pedregosa, F., Mueller, A., Grisel, O., ... & Varoquaux, G. (2013). API design for machine learning software: experiences from the scikit-learn project. arXiv preprint arXiv:1309.0238. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1309.0238
Cakir, E. (2013). The association between metabolic syndrome components and hair loss both male and female individuals. Hair Ther Transplant, 3(110), 2167-0951. DOI: 10.4172/2167-0951.1000110
Cavicchia, P. P., Steck, S. E., Hurley, T. G., Hussey, J. R., Ma, Y., Ockene, I. S., & Hébert, J. R. (2009). A new dietary inflammatory index predicts interval changes in serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. The Journal of nutrition, 139(12), 2365-2372. DOI: 10.3945/jn.109.114025
Chrysohoou, C., Panagiotakos, D. B., Pitsavos, C., Das, U. N., & Stefanadis, C. (2004). Adherence to the Mediterranean diet attenuates inflammation and coagulation process in healthy adults: The ATTICA Study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 44(1), 152-158. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.03.039
Darbandi, M., Hamzeh, B., Ayenepour, A., Rezaeian, S., Najafi, F., Shakiba, E., & Pasdar, Y. (2021). Anti-inflammatory diet consumption reduced fatty liver indices. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 22601. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-98685-3
De Punder, K., & Pruimboom, L. (2013). The dietary intake of wheat and other cereal grains and their role in inflammation. Nutrients, 5(3), 771-787. DOI: 10.3390/nu5030771
Duncan, F. J., Silva, K. A., Johnson, C. J., King, B. L., Szatkiewicz, J. P., Kamdar, S. P., ... & Everts, H. B. (2013). Endogenous retinoids in the pathogenesis of alopecia areata. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 133(2), 334-343. DOI: 10.1038/jid.2012.344
Esmaillzadeh, A., Kimiagar, M., Mehrabi, Y., Azadbakht, L., Hu, F. B., & Willett, W. C. (2007). Dietary patterns and markers of systemic inflammation among Iranian women. The Journal of nutrition, 137(4), 992-998. DOI: 10.1093/jn/137.4.992
Fateh, H. L., Nachvak, M., Abdollahzad, H., Rezaeian, S., Darand, M., & Bagheri, A. (2022). Nutritional status of under six years old children in Kalar city, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. BMC Public Health, 22(1), 1668. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-022-14071-2
Ganzetti, G., Simonetti, O., Campanati, A., Giuliodori, K., Scocco, V., Brugia, M., ... & Offidani, A. (2015). Osteopontin: a new facilitating factor in alopecia areata pathogenesis? Acta Dermatovenerologica Croatica, 23(1), 19-19.
Ghaffarpour, M., Houshiar-Rad, A., & Kianfar, H. J. T. N. O. K. (1999). The manual for household measures, cooking yields factors and edible portion of foods. Tehran: Nashre Olume Keshavarzy, 7(213), 42-58.
Gilhar, A., Laufer-Britva, R., Keren, A., & Paus, R. (2019). Frontiers in alopecia areata pathobiology research. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 144(6), 1478-1489. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.08.035
González‐González, J. G., Mancillas‐Adame, L. G., Fernández‐Reyes, M., Gómez‐Flores, M., Lavalle‐González, F. J., Ocampo‐Candiani, J., & Villarreal‐Pérez, J. Z. (2009). Androgenetic alopecia and insulin resistance in young men. Clinical endocrinology, 71(4), 494-499. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2008.03508.x
Hajianfar, H., Mirmossayeb, O., Mollaghasemi, N., Nejad, V. S., & Arab, A. (2022). Association between dietary inflammatory index and risk of demyelinating autoimmune diseases. International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research. DOI: 10.1024/0300-9831/a000754
Hassan, M. M., & Taher, S. A. (2022). Analysis and classification of autism data using machine learning algorithms. Science Journal of University of Zakho, 10(4), 206-212. DOI: 10.25271/sjuoz.2022.10.4.1036
Hassan, M. M., & Ahmed, D. (2023). BAYESIAN DEEP LEARNING APPLIED TO LSTM MODELS FOR PREDICTING COVID-19 CONFIRMED CASES IN IRAQ. Science Journal of University of Zakho, 11(2), 170-178. DOI: 10.25271/sjuoz.2023.11.2.1037
Holt, E. M., Steffen, L. M., Moran, A., Basu, S., Steinberger, J., Ross, J. A., ... & Sinaiko, A. R. (2009). Fruit and vegetable consumption and its relation to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress in adolescents. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 109(3), 414-421. DOI: 10.1016/j.jada.2008.11.036
Ito, T. (2012). Advances in the management of alopecia areata. The Journal of Dermatology, 39(1), 11-17. DOI: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01476.x
Jenkins, D. J., Kendall, C. W., Marchie, A., Faulkner, D. A., Wong, J. M., de Souza, R., ... & Connelly, P. W. (2003). Effects of a dietary portfolio of cholesterol-lowering foods vs lovastatin on serum lipids and C-reactive protein. Jama, 290(4), 502-510. DOI: 10.1001/jama.290.4.502
Kaluza, J., Harris, H., Melhus, H., Michaëlsson, K., & Wolk, A. (2018). Questionnaire-based anti-inflammatory diet index as a predictor of low-grade systemic inflammation. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7330
Kohli, M., Kar, A. K., Bangalore, A., & Ap, P. (2022). Machine learning-based ABA treatment recommendation and personalization for autism spectrum disorder: an exploratory study. Brain Informatics, 9(1), 16. DOI: 10.1186/s40708-022-00164-6
Madani, S., & Shapiro, J. (2000). Alopecia areata update. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 42(4), 549-566. DOI: 10.1067/mjd.2000.103909
Masters, R. C., Liese, A. D., Haffner, S. M., Wagenknecht, L. E., & Hanley, A. J. (2010). Whole and refined grain intakes are related to inflammatory protein concentrations in human plasma. The Journal of nutrition, 140(3), 587-594. DOI: 10.3945/jn.109.116640
Matilainen, V., Koskela, P., & Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S. (2000). Early androgenetic alopecia as a marker of insulin resistance. The Lancet, 356(9236), 1165-1166. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02763-X
Matilainen, V., Laakso, M., Hirsso, P., Koskela, P., Rajala, U., & Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S. (2003). Hair loss, insulin resistance, and heredity in middle-aged women. A population-based study. European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation, 10(3), 227-231. DOI: 10.1097/01.hjr.0000070200.72977.c6
Mirmiran, P., Esfahani, F. H., Mehrabi, Y., Hedayati, M., & Azizi, F. (2010). Reliability and relative validity of an FFQ for nutrients in the Tehran lipid and glucose study. Public health nutrition, 13(5), 654-662. DOI: 10.1017/S1368980009991698
Mirmirani, P., Willey, A., Headington, J. T., Stenn, K., McCalmont, T. H., & Price, V. H. (2005). Primary cicatricial alopecia: histopathologic findings do not distinguish clinical variants. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 52(4), 637-643. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2004.07.069
Mohammed, S. J., & Tayfor, N. B. (2024). THE PREDICTION OF HEART DISEASE USING MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS. Science Journal of University of Zakho, 12(3), 285-293. DOI: 10.25271/sjuoz.2024.12.3.1270
Moludi, J., Fateh, H. L., Pasdar, Y., Moradinazar, M., Sheikhi, L., Saber, A., ... & Dey, P. (2022). Association of dietary inflammatory index with chronic kidney disease and kidney stones in Iranian adults: a cross-sectional study within the Ravansar non-communicable diseases cohort. Frontiers in nutrition, 9, 955562. DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.955562
Mumcuoglu, C., Ekmekci, T. R., & Sema, U. C. A. K. (2011). The investigation of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in male patients with early-onset androgenetic alopecia. European journal of dermatology, 21(1), 79-82. DOI: 10.1684/ejd.2010.1193
Norde, M. M., Fisberg, R. M., Marchioni, D. M. L., & Rogero, M. M. (2020). Systemic low-grade inflammation associated lifestyle, diet, andgenetic factors: a population-based cross-sectional study. Nutrition, 70, 6. DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2019.110596
Olsen, E. A., & Canfield, D. (2016). SALT II: a new take on the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for determining percentage scalp hair loss. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 75(6), 1268-1270. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.08.042
Paleyes, A., Urma, R. G., & Lawrence, N. D. (2022). Challenges in deploying machine learning: a survey of case studies. ACM computing surveys, 55(6), 1-29. DOI: 10.1145/3533378
Parmar, A., Katariya, R., & Patel, V. (2019). A review on random forest: An ensemble classifier. In International conference on intelligent data communication technologies and internet of things (ICICI) 2018 (pp. 758-763). Springer International Publishing. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-03146-6_86
Pranckevičius, T., & Marcinkevičius, V. (2017). Comparison of naive bayes, random forest, decision tree, support vector machines, and logistic regression classifiers for text reviews classification. Baltic Journal of Modern Computing, 5(2), 221. DOI: 10.22364/bjmc.2017.5.2.05
Rateb, A. A., Mohammed, F. N., Sayed, K. S., Hegazy, R. A., Al Agha, R. R., Rashed, L. A., & Sayed, S. S. (2015). Gene expression of osteopontin in alopecia areata? A case-controlled study. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 28(2), 84-90. DOI: 10.1159/000363147
Saif, G. A. B., Alotaibi, H. M., Alzolibani, A. A., Almodihesh, N. A., Albraidi, H. F., Alotaibi, N. M., & Yosipovitch, G. (2018). Association of psychological stress with skin symptoms among medical students. Saudi medical journal, 39(1), 59. DOI: 10.15537/smj.2018.1.21231
Salih, M. S., & Pasha, S. A. (2024). UTILIZING NUTRITIONAL AND LIFESTYLE DATA FOR PREDICTING STUDENT ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE: A MACHINE LEARNING APPROACH. Science Journal of University of Zakho, 12(3), 356-360.33. Verma, A. K., Pal, S., & Tiwari, B. B. (2020). Skin disease prediction using ensemble methods and a new hybrid feature selection technique. Iran Journal of Computer Science, 3(4), 207-216. DOI: 10.25271/sjuoz.2024.12.3.1288
Samraj, A. N., Pearce, O. M., Läubli, H., Crittenden, A. N., Bergfeld, A. K., Banda, K., ... & Varki, A. (2015). A red meat-derived glycan promotes inflammation and cancer progression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(2), 542-547. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1417508112
Saraswathi, C., & Pushpa, B. (2023). Machine Learning Algorithm for Classification of Alopecia Areata from Human Scalp Hair Images. In Computational Vision and Bio-Inspired Computing: Proceedings of ICCVBIC 2022 (pp. 269-288). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-19-9819-5_21
Shin, P. K., Park, S. J., Kim, M. S., Kwon, D. Y., Kim, M. J., Kim, K., ... & Choi, S. W. (2020). A traditional Korean diet with a low dietary inflammatory index increases anti-inflammatory IL-10 and decreases pro-inflammatory NF-κB in a small dietary intervention study. Nutrients, 12(8), 2468. DOI: 10.3390/nu12082468
Shivappa, N., Bosetti, C., Zucchetto, A., Montella, M., Serraino, D., La Vecchia, C., & Hébert, J. R. (2015). Association between dietary inflammatory index and prostate cancer among Italian men. British journal of nutrition, 113(2), 278-283. DOI: 10.1017/S0007114514003572
Shivappa, N., Godos, J., Hébert, J. R., Wirth, M. D., Piuri, G., Speciani, A. F., & Grosso, G. (2018). Dietary inflammatory index and cardiovascular risk and mortality—a meta-analysis. Nutrients, 10(2), 200. DOI: 10.3390/nu10020200
Shivappa, N., Prizment, A. E., Blair, C. K., Jacobs Jr, D. R., Steck, S. E., & Hébert, J. R. (2014). Dietary inflammatory index and risk of colorectal cancer in the Iowa Women's Health Study. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 23(11), 2383-2392. DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0537
Shivappa, N., Steck, S. E., Hurley, T. G., Hussey, J. R., & Hébert, J. R. (2014). Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public health nutrition, 17(8), 1689-1696. DOI: 10.1017/S1368980013002115
Shivappa, N., Steck, S. E., Hurley, T. G., Hussey, J. R., Ma, Y., Ockene, I. S., ... & Hébert, J. R. (2014). A population-based dietary inflammatory index predicts levels of C-reactive protein in the Seasonal Variation of Blood Cholesterol Study (SEASONS). Public health nutrition, 17(8), 1825-1833. DOI: 10.1017/S1368980013002565
Šín, P., Hokynková, A., Marie, N., Andrea, P., Krč, R., & Podroužek, J. (2022). Machine learning-based pressure ulcer prediction in modular critical care data. diagnostics, 12(4), 850. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12040850
Soheila, N., Behzad, I., Mehdi, G., Fahimeh, A., & Niloufar, N. (2018). The influence of osteopontin on the pathogenesis of alopecia areata and its association with disease severity. Iranian Journal of Dermatology, 21(2), 43-47. DOI: 10.22034/ijd.2018.98350
Somani, N., & Bergfeld, W. F. (2008). Cicatricial alopecia: classification and histopathology. Dermatologic therapy, 21(4), 221-237. DOI: 10.1111/j.1529-8019.2008.00203.x
Suo, L., Sundberg, J. P., & Everts, H. B. (2015). Dietary vitamin A regulates wingless-related MMTV integration site signaling to alter the hair cycle. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 240(5), 618-623. DOI: 10.1177/1535370214557220
Thompson, J. M., Mirza, M. A., Park, M. K., Qureshi, A. A., & Cho, E. (2017). The role of micronutrients in alopecia areata: a review. American journal of clinical dermatology, 18, 663-679. DOI: 10.1007/s40257-017-0285-x
Upritchard, J. E., Sutherland, W. H., & Mann, J. I. (2000). Effect of supplementation with tomato juice, vitamin E, and vitamin C on LDL oxidation and products of inflammatory activity in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes care, 23(6), 733-738. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.23.6.733
Wareham, N. J., Jakes, R. W., Rennie, K. L., Schuit, J., Mitchell, J., Hennings, S., & Day, N. E. (2003). Validity and repeatability of a simple index derived from the short physical activity questionnaire used in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Public health nutrition, 6(4), 407-413. DOI: 10.1079/PHN2002439
Wood, A. C., Graca, G., Gadgil, M., Senn, M. K., Allison, M. A., Tzoulaki, I., ... & Herrington, D. (2023). Untargeted metabolomic analysis investigating links between unprocessed red meat intake and markers of inflammation. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 118(5), 989-999. 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.08.018
Wood, L. G., Shivappa, N., Berthon, B. S., Gibson, P. G., & Hebert, J. R. (2015). Dietary inflammatory index is related to asthma risk, lung function and systemic inflammation in asthma. Clinical & Experimental Allergy, 45(1), 177-183. DOI: 10.1111/cea.12323
Authors
Copyright (c) 2025 Mohammed Sarwat M Salih, Hawal Lateef Fateh, Soran Abdulkarim Pasha , and Hassan M Tawfiq

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License [CC BY-NC-SA 4.0] that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work, with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online.