MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF MALE DONKEY REPRODUCTIVE DUCTS: FROM DEFERENT DUCTS TO EJACULATORY PATHWAYS
Abstract
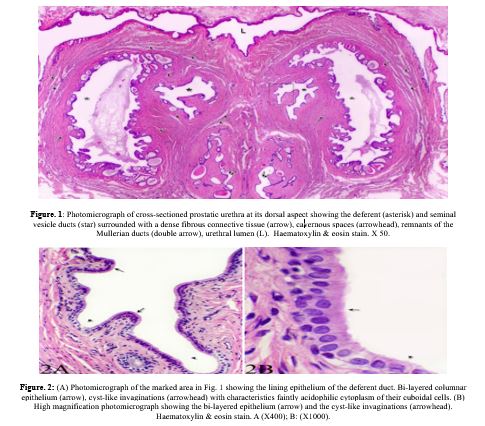
The anatomical and histological characteristics of the terminal deferent ducts, excretory ducts of the seminal vesicles, and ejaculatory ducts were examined in detail. The terminal deferent duct, located ventromedially to the excretory duct of the seminal vesicle, exhibited a small, irregular lumen with cyst-like invaginations into the vascular, fibromuscular connective tissue. Its lumen was lined by bi-layered columnar epithelium, with principal cuboidal cells and occasional basal flat cells. The connective tissue of the cranial deferent duct contained collagen, elastic fibers, and smooth muscle, transitioning towards diminished smooth muscle at the duct's terminal region. The ducts from either side merged to form common ejaculatory ducts, which entered the urethra at the Colliculus seminalis. At this junction, the epithelium changed to either stratified columnar or cuboidal types. The ejaculatory ducts exhibited lumens characterized by branched folds, which were lined with stratified columnar epithelium and reinforced by a dense network of collagenous and elastic connective tissue. Scanning electron microscopy revealed that the luminal surface of the ejaculatory duct was folded, irregularly oval, had nearly hexagonal epithelial cells with distinct borders, and abundant microvilli on the luminal surfaces. These findings provide a comprehensive understanding of the structural organization of these ducts and their role in the male reproductive system
Full text article
References
Abd-Elhafeez, H. H., Al Sulivany, B. S. A ., Salah, A. S., Ali, M., Mohamed, N. E., Soliman, S. A. (2024). microscopic architecture of the respiratory and conducting system of the lung of the nile monitor (varanus niloticus). Science Journal of University of Zakho 12. https://doi.org/10.25271/sjuoz.2024.12.3.1362
Abou-Elhamd, A. S., AbdelRahman, Y., Selim A. (2019). Pelvic Urethra and its Associated Glands in Donkey (Equus asinus): Histological and Histochemical Findings with Special Reference to their Seasonal Variations. Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research 9:134-143.
Abou-Elhamd, A.S., AbdelRahman, Y.A., Selim, A.A. (2020). Histological and Histochemical Studies on the Seminal Vesicles of Donkey (Equus asinus): with Special Reference to their Seasonal Variations. Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research 10:126-134.
Abou-Elhamd, A.S., Salem, A.O., Selim, A.A. (2012). Histological and Histochemical Studies on the Ampulla of the Deferent Duct of Donkey (Equus asinus). Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research 2:261-270.
Abou-Elhamd, A. S., Salem, A.O., Selim, A.A. (2013). Histomorphological Studies on the Prostate Gland of Donkey Equus Asinus during Different Seasons. Journal of Histology:1-19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/643287
Abou-Elhamd, A.S., Selim, A., Rahman, Y.A. (2021). Gross, Histological and Scanning Electron Studies on the Bulbourethral Gland of Donkey (Equus asinus) during Different Seasons. Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research 11:147-157.
Abou-Elmagd, A., Kelany, A.M. (1992). Electron microscopical observation on the active vesicular glands of buffalo. Assiut Vet Med J 28:68-80.
Abou-Elmagd, A., Wrobel, K-H. (1990). The epithelial lining of the bovine ejaculatory duct. Cells Tissue Organs 139:60-65. https://doi.org/10.1159/000146979
Cossu, M., Marcello, M., Usai, E., Riva, F., Riva, A. (1983). Fine structure of the epithelium of the human ejaculatory duct. Cells Tissues Organs 116:225-233. https://doi.org/10.1159/000145746
Cross, C. E. (1995). Bloom and Fawcett: A Textbook of Histology. JAMA 274:352-352.
Crossmon, G. (1937). A modification of Mallory’s connective tissue with a discussion of principles involved. Anat. Rec. 69:33-38. Cited by Böck P: In Romeis Mikroskopishe Technik. 17 Aufl. Urban und Schwarzenberg. München-Wien-Baltimore 1989.
Eroschenko, V. P., Di Fiore, M.S. (2013). DiFiore's atlas of histology with functional correlations: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Eurell, J.A., Frappier, B.L. (2006). Male reproductive system. In Dellman's textbook of veterinary histology., 6th ed. State Avenue, Ames, Iowa, USA: Blackwell Publishing.
Gomori, G. (1937). Silver Impregnation of Reticulum in Paraffin Sections. Am J Pathol 13:993-1002 1005.
Gurung, P., Yetiskul, E. and Jialal, I. (2023). Physiology, male reproductive system. In: StatPearls [Internet]: Statpearls publishing.
Hafez, E. S. E., Hafez, B. (2013). Reproduction in farm animals: John Wiley & Sons.
Harris, H. F. (1900). On the rapid conversion of haematoxylin into haematin in staining reactions. J. Appl. Microsc. Lab. methods; 3: 777. Cited by Suvarna, Kim S Layton,
Christopher, B. and John D. (2013). Bancroft's theory and practice of histological technique. Chirchill LivingStone.
Junqueira, L. (2005). Basic histology: text and atlas. In: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Junqueira, L. C., Carneiro, J. and Kelley, R. O. (1998). Urinary system. In basic histology., 9th ed. Stamford Connecticut.: Appleton & Lange.
Mathangasinghe, Y., Samaranayake, U.M., Dolapihilla, B.N., Anthony, D.J., Malalasekera, A.P. (2020). Morphology of ejaculatory ducts: A systematic review. Clinical Anatomy.33:1164-1175. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.23557
Mustafa, FE-ZA., Al Sulivany, B. S. A. (2025(. histological, histochemical, and immunohistochemical characterization of the efferent ductules of the dove: histological studies of the efferent ductules of the dove. science Journal of University of Zakho 13:45-51. https://doi.org/10.25271/sjuoz.2025.13.1.1399
Noda, T., Ikawa, M. (2019). Physiological function of seminal vesicle secretions on male fecundity. Reproductive medicine and biology 18:241-246. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmb2.12282
Robaire, B. (1988). Efferent ducts, epididymis and vas deferens: structure, functions and their regulation. In: The Physiology of Reproduction/Raven Press.
Ross, M.H., Pawlina, W. (2006). A text and atlas with correlated cell and molecular biology. Williams and Wilkins 6:529-533.
Standring, S.(2021). Gray's Anatomy E-Book: Gray's Anatomy E-Book: Elsevier Health Sciences.
Standring, S., Ellis, H., Healy, J., Johnson, D., Williams, A., Collins, P., Wigley, C. (2005). Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. American journal of neuroradiology 26:2703.
Steger, K., Weidner, W. (2011). Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System. In: Chapple CR, Steers WD, editors. Practical Urology: Essential Principles and Practice: Essential Principles and Practice. London: Springer London. 57-68.
Verhoeff, F. H. (1908). Some new staining methods of wide applicability. Including a rapid differential stain for elastic tissue. J. Am. Med. Assoc., 50, 876. Cited by Bancroft, J. D. and Steven, A. (1996). DOI:10.1001/jama.1908.25310370042004a
Authors
Copyright (c) 2025 Alaa Abou-Elhamd

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License [CC BY-NC-SA 4.0] that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work, with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online.