THE ROLE OF SILICA NANOPARTICLES IN MODULATING GROWTH PERFORMANCE, ENZYME ACTIVITY, AND HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION IN MUSCLE TISSUE OF COMMON CARP (Cyprinus carpio. L)
Abstract
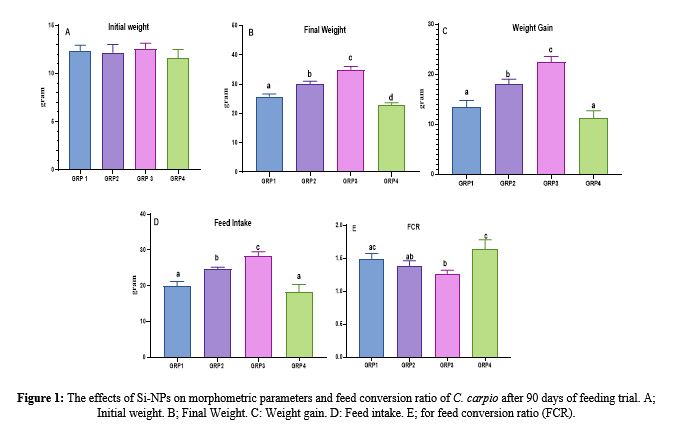
This study investigated the effects of dietary supplementation with silicon nanoparticles (Si-NPs) on the growth performance, trace element concentrations, and serum enzyme activity of Cyprinus carpio (C. carpio) over a 90-day feeding trial. Four experimental diets with varying levels of Si-NPs were prepared: the first group (GRP1) was given 0 mg/kg, the second group (GRP2) received 1 mg/kg, the third group (GRP3) was supplemented with 2 mg/kg, and the fourth group (GRP4) had 3 mg/kg of Si-NPs. Results revealed that moderate levels of Si-NPs (1-2 mg/kg) significantly improved growth performance (p < 0.05), with GRP3 exhibiting the highest final weight (35 ± 0.44 g), weight gain (22.4 ± 0.5 g), and feed conversion ratio (1.269 ± 0.023). In contrast, GRP4 (3 mg/kg) showed reduced growth. Trace element analysis demonstrated that Si-NPs at 1-2 mg/kg enhanced the bioavailability of essential elements such as Sodium (Na), Iron (Fe), Magnesium (Mg), and Zinc (Zn), while higher doses disrupted trace element homeostasis. Serum enzyme activities, including Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Acid Phosphatase (ACP), Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP), and Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH), were significantly reduced in GRP2 and GRP3, suggesting a protective effect against oxidative stress and tissue damage. However, enzyme activities of GRP4 returned to control values, implying a threshold effect. The research indicates the beneficial effect of Si-NPs as a food supplement for growth enhancement, nutrient assimilation, and protecting the fish against oxidative stress if dosing is carefully adjusted to avoid toxicity.
Full text article
References
REFERENCES:
Ahmed, S. S., & Hasan, M. A. (2019). Determination of headetermination of some heavy metals in three fish species from duhok city markets in Kurdistan of Iraq. Science Journal of University of Zakho, 7(4), 152–157. https://DOI.org/10.25271/sjuoz.2019.7.4.621
Al Sulivany, B., Owais, M., Fazal, R., Asad, F., Hussein, N., & Selamoglu, Z. (2024). Seasonal effects of protein levels on common carp (Cyprinus carpio) body composition. Iraqi Journal of Aquaculture, 21(2), 111–127. https://DOI.org/10.58629/ijaq.v21i2.520
Ali, A., Saeed, S., Hussain, R., Saif, M. S., Waqas, M., Asghar, I. Hasan, M. (2024). Exploring the impact of silica and silica-based nanoparticles on serological parameters, histopathology, organ toxicity, and genotoxicity in Rattus norvegicus. Applied Surface Science Advances, 19, 100551. https://DOI.org/10.1016/j.apsadv.2023.100551
Al-Imarah, F., Al-Najare, G., Al-Faiz, N., & Younis, K. (2024). Distribution of heavy metals in core sediments of Southern Iraq Waterways. Technology audit and production reserves, 5(3 (79)), 25-30. https://DOI.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.314134
Al-Khayri, J. M., Rashmi, R., Surya Ulhas, R., Sudheer, W. N., Banadka, A., Nagella, P., ... & Almaghasla, M. I. (2023). The role of nanoparticles in response of plants to abiotic stress at physiological, biochemical, and molecular levels. Plants, 12(2), 292.
Balali-Mood, M., Naseri, K., Tahergorabi, Z., Khazdair, M. R., & Sadeghi, M. (2021). Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Frontiers in pharmacology, 12, 643972. https://DOI.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643972
Banday, U. Z., Swaleh, S. B., & Usmani, N. (2019). Insights into the heavy metal-induced immunotoxic and genotoxic alterations as health indicators of Clarias gariepinus inhabiting a rivulet. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 183, 109584. https://DOI.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109584
Ceccotti, C., Al-Sulaivany, B. S. A., Al-Habbib, O. A. M., Saroglia, M., Rimoldi, S., & Terova, G. (2019). Protective Effect of Dietary Taurine from ROS Production in European Seabass under Conditions of Forced Swimming. Animals, 9(9), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090607
Chan, C. Y., Tran, N., Pethiyagoda, S., Crissman, C. C., Sulser, T. B., & Phillips, M. J. (2019). Prospects and challenges of fish for food security in Africa. Global Food Security, 20: 17–25. https://DOI.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2018.12.002
Chen, Y., Zhang, X., & Li, J. (2020). Toxicity of nanoparticles in aquatic organisms: A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(12), 13384–13398. https://DOI.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07877-3.
Das, P. S., Rohani, M. F., Al Sulivany, B. S., Nibir, S. S., Juthi, R. A., Satter, A., ... & Ismael, S. S. (2025). Dietary silica nanoparticle ameliorates the growth performance and muscle composition of stinging catfish heteropneustes fossilis. Science Journal of University of Zakho, 13(1), 33-39. https://DOI.org/10.25271/sjuoz.2025.13.1.1394
El-Naby, A. S. A., El Asely, A. M., Hussein, M. N., Khattaby, A. E. R. A., & Abo-Al-Ela, H. G. (2025). Impact of dietary Biocide clay on growth, physiological status, and histological indicators of the liver and digestive tract in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Scientific Reports, 15(1), 5311. https://DOI.org/10.1038/s41598-025-89042-9
Farooq, M. A., Hannan, F., Islam, F., Ayyaz, A., Zhang, N., Chen, W., ... & Zhou, W. (2022). The potential of nanomaterials for sustainable modern agriculture: present findings and future perspectives. Environmental Science: Nano, 9(6), 1926-1951.
Gao, Y., Wang, X., & Liu, H. (2021). Silicon nanoparticles enhance nutrient absorption and growth performance in fish. Aquaculture Nutrition, 27(3), 567-576. https://DOI.org/10.1111/anu.13245.
Ghafarifarsani, H., Hoseinifar, S. H., Raeeszadeh, M., Vijayaram, S., Rohani, M. F., Van Doan, H., & Sun, Y. Z. (2024). Comparative effect of chemical and green zinc nanoparticles on the growth, hematology, serum biochemical, antioxidant parameters, and immunity in serum and mucus of goldfish, Carassius auratus (Linnaeus, 1758). Biological Trace Element Research, 202(3), 1264-1278. DOI: 10.1007/s12011-023-03753-6.
Hamed, A., & Badran, S. R. (2024). The role of rice husk in Oreochromis niloticus safety enhancement by bio-adsorbing copper oxide nanoparticles following its green synthesis: an endeavor to advance environmental sustainability. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 23730. https://DOI.org/10.1038/s41598-024-74113-0
Hoseini, S. M., Al Sulivany, B. S. A., Kordmahalleh, A. A., Abdollahpour, H., Rajabiesterabadi, H. and Morteza Yousefi. (2025). Effects of dietary citric acid, lactic acid, and potassium sorbate mixture on growth performance and intestinal immunological parameters in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) juveniles. World Aquaculture Society, Wiley, 56, 1, 1–18.
Hou, J., Zhang, Y., & Li, X. (2011). Oxidative stress and inflammation induced by nanoparticles in aquatic organisms. Aquatic Toxicology, 105(3-4), 78–86. https://DOI.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.05.014.
Hussain, S. M., Naeem, E., Ali, S., Adrees, M., Riaz, D., Paray, B. A., & Naeem, A. (2024). Evaluation of growth, nutrient absorption, body composition and blood indices under dietary exposure of iron oxide nanoparticles in Common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 108(2), 366–373. https://DOI.org/10.1111/jpn.13898
Jan, A. T., Azam, M., Siddiqui, K., Ali, A., Choi, I., & Haq, Q. M. R. (2015). Heavy metals and human health: mechanistic insight into toxicity and counter defence system of antioxidants. International journal of molecular sciences, 16(12), 29592-29630.
Khalefa, H.S., AbuBakr, H.O., Aljuaydi, S.H. (2024). Aquatic assessment of the chelating ability of Silica-stabilized magnetite nanocomposite to lead nitrate toxicity with emphasis on their impact on hepatorenal, oxidative stress, genotoxicity, histopathological, and bioaccumulation parameters in Oreochromis niloticus and Clarias gariepinus. BMC Vet Res 20, 262. https://DOI.org/10.1186/s12917-024-04094-9
Laz-Figueroa, K., Valenzuela-Cobos, J., & Guevara-Viejó, F. (2024). Assessing Feeding Regimes and Its Impact on Tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) Performance and Aquaculturist Perceptions in Aquaculture. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology & Fisheries, 28(6). 10.21608/EJABF.2024.393891.
Li, Z., Wang, Y., & Chen, X. (2019). Effects of nanoparticle size and concentration on fish growth and metabolism. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health, 31(2), 123-132. https://DOI.org/10.1002/aah.10056
Liu, X., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2020). Antioxidant effects of silicon nanoparticles in fish: A review. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 98, 123–130. https://DOI.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.01.012.
Mahboub, H. H., Gad, W. M., Aziz, E. K. (2024). Silica nanoparticles alleviate the immunosuppression, oxidative stress, and biochemical, behavioral, and histopathological alterations induced by Aeromonas veronii infection in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Fish Physiol Biochem 50, 767–783. https://DOI.Org/10.1007/s10695-023-01274-6
Mehta, S. (2025). Introduction to Nanoparticles, Synthesis Characterization and Clinical Status. In Nanoparticles in the Management of Atherosclerosis: A Machine-Generated Literature Overview (pp. 83–214). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland
Min, Y., Suminda, G. G. D., Heo, Y., Kim, M., Ghosh, M., & Son, Y. O. (2023). Metal-based nanoparticles and their relevant consequences on cytotoxicity cascade and induced oxidative stress. Antioxidants, 12(3), 703.
Owais, M., Al Sulivany, B. S. A., Fazal, R. M., & Abdellatif, M. (2024b). Evaluating Growth and Nutrient Composition of African Catfish Under Different Salinities. Science Journal of University of Zakho, 12(4), 407–412. https://DOI.org/10.25271/sjuoz.2024.12.4.1355
Owais, M., Al Sulivany, B., Abdulhalim, B. A., & Mehroz, R. (2024a). The Pangas Catfish Pangasius pangasius; Growth Efficiency and Nutritional Composition Under Variety of Saltwater Challenges. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology & Fisheries, 28(6). 10.21608/ejabf.2024.389994.
Abdulrahman, P, M, S.; Al Sulivany, B. S. A. (2025). Dietary Quercus infectoria Mitigates Lead Nitrate Toxicity in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio): Impacts on Growth Performance, Condition Factors, Weight Length Relationship, Hematological Responses, and Detoxification Potential During 60-Day Exposure. Egyprian Journal of Aquatic Biology and Fisherie, 29(2); 383-405. DOI: 10.21608/ejabf.2025.416695
Rahman, A. N. A., Mahboub, H. H., Ezz-Eldin, R. M., Abdelwarith, A. A., Younis, E. M., Khamis, T., ... & Reyad, Y. A. (2025). Lead toxicity in African catfish: Promising role of magnetite nanogel against etho-neurological alterations, antioxidant suppression, gene toxicity, and histopathological/immunohistochemical disruptions. Aquaculture, 594, 741411. https://DOI.Org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.741411
Reda, R. M., Zaki, E. M., AA Aioub, A., Metwally, M. M., Yassin, A. M., & Mahsoub, F. (2025). Behavioural, biochemical, immune, and histological responses of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus, 1758) to lead, mercury, and pendimethalin exposure: individual and combined effects. Environmental Sciences Europe, 37(1), 11. https://DOI.org/10.1186/s12302-024-01047-9
Roy, T. K., Islam, M. S., Mahiddin, N. A., Hossain, S. A., Biswas, T., Antu, U. B., ... & Ismail, Z. (2025). Application of Nanoparticles (NPs) to Ameliorate Abiotic Stress in Economically Important Crop Species: a Potential Review. Journal of Crop Health, 77(1), 1–20. 10.1007/s10343-024-01069-6.
Singha, K. P., Shamna, N., Sahu, N. P., Sardar, P., Harikrishna, V., Thirunavukkarasar, R., Chowdhury, D. K., Maiti, M. K., & Krishna, G. (2021). Optimum dietary crude protein for the culture of genetically improved farmed tilapia (GIFT), Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) juveniles in low inland saline water: Effects on growth, metabolism and gene expression. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 271, 114713. https://DOI.Org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114713
Tacon, A. G. J., Metian, M., & Hasan, M. R. (2020). Feed conversion efficiency in aquaculture: A global review. Reviews in Aquaculture, 12(2), 677–702. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12343 Wang, L., Zhang, H., & Li, Q. (2021). The role of nanoparticles in improving feed efficiency in aquaculture. Aquaculture Research, 52(3), 987–996. https://DOI.Org/10.1111/are.14956
Torrealba, D., More-Bayona, J. A., Wakaruk, J., & Barreda, D. R. (2019). Innate immunity provides health biomarkers for teleosts exposed to nanoparticles. Frontiers in immunology, 9, 3074.
Wagner, J., and Stanton, T. L. (2012). Formulating RationsWith the Pearson Square., CO: Colorado State University.
Wang, Y. L., Lee, Y. H., Chou, C. L., Chang, Y. S., Liu, W. C., & Chiu, H. W. (2024). Oxidative stress and potential effects of metal nanoparticles: A review of biocompatibility and toxicity concerns. Environmental Pollution, 123617.
Zhang, J., Eggen, M., Peruzzi, S., Klokkerengen, R., Sundfør, E., Odei, D. K., ... & Mota, V. C. (2024). Effects of prolonged application of peracetic acid-based disinfectant on recirculating aquaculture systems stocked with Atlantic salmon parr. Science of The Total Environment, 173762. https://DOI.ORG/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173762
Zhang, X., Li, Y., & Wang, Z. (2022). Toxicity mechanisms of nanoparticles in aquatic organisms. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 41(4), 789–799. https://DOI.Org/10.1002/etc.5289
Zhao, L., Wang, J., & Liu, Y. (2022). Modulation of gut microbiota by nanoparticles in fish: Implications for growth and health. Aquaculture, 548, 737–745. https://DOI.ORg/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737745
Authors
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Owais, Dilsher Ahmed Mohammed, Husni A Mhammad, Basim S A Al Sulivany, Seval Dernekbaşı, Rana Meroz Fazal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License [CC BY-NC-SA 4.0] that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work, with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online.