THE EFFECT OF THE NOISE ON THE BEHAVIOUR OF FEMALE ALBINO RATS
Abstract
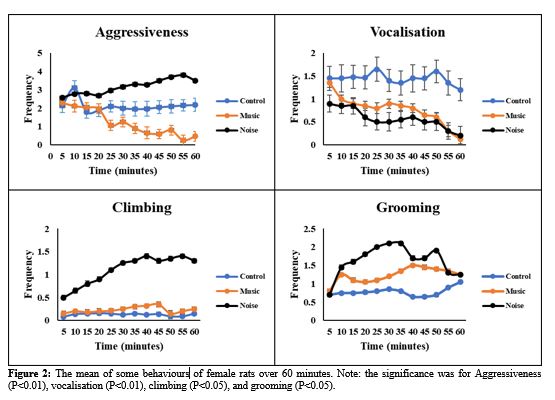
Noise is considered an important environmental factor that can affect animal behaviour and productivity. Its impact varies depending on the noise intensity, pattern, duration, and frequency. This research was undertaken to determine the effect of noise stress and playing music on improving the behaviour of female rats. Seventy-five female albino rats were divided into 3 groups, with 25 rats per group. The research groups were Control (no sound exposure), classical music, and noise stress. The sound level for the classic was 80 dB with a frequency of 1 kHz using an MP3 player. The sound level of stress exceeded 150 dB. The results revealed that using classical music led to a significant reduction in the frequency of aggressive behaviours (P<0.01) and an increase in vocalisations (P<0.01). In addition, music and noise stress significantly increased grooming (P<0.05) and climbing behaviour (P<0.05). Furthermore, exposure to the use of music caused increased drinking and feeding behaviours significantly (P<0.01), whereas lying and standing behaviours were decreased (P<0.01). In conclusion, playing music, especially classical music, benefits rats’ welfare by improving their behaviour, as evidenced of decreased vocalization and increased feeding and drinking.
Full text article
References
Akiyama, K., & Sutoo, D. E. (2011). Effect of different frequencies of music on blood pressure regulation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neuroscience letters, 487(1), 58-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.073
Algers, B., Ekesbo, I., & Stromberg, S. (1978). The impact of continuous noise on animal health. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, Suppl. 67, p. 1-26. https://doi.org/10.5555/19780444878
Apukhtin, K. V., Shevlyakov, A. D., Kotova, M. M., Amikishiev, S. V., Riga, V. D., Volgin, A. D., & Kalueff, A. V. (2024). Analysis of Rodent Grooming and Its Microstructure in Modern Neurobiological Studies. Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology, 60(3), 1125-1143. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093024030219
Bleibel, M., El Cheikh, A., Sadier, N. S., & Abou-Abbas, L. (2024). The effect of music therapy on cognitive functions in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Alzheimer's research & therapy, 15(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-023-01214-9
Bodhika, J. A. P. & Jayakody, J. R. I. A. (2018). A study on behavioural effects of laboratory rats (albino wistar) after the sub-chronic noise stress. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 6(3), 739. http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20180587
Brouček, J. (2014). Effect of noise on performance, stress, and behaviour of animals. Slovak journal of animal science, 47(2), 111-123.
Brotons, M., & Marti, P. (2003). Music therapy with Alzheimer's patients and their family caregivers: a pilot project. Journal of music therapy, 40(2), 138-150. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmt/40.2.138
Burn, C. C. (2008). What is it like to be a rat? Rat sensory perception and its implications for experimental design and rat welfare. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 112(1-2), 1-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2008.02.007
Burns, J. L., Labbé, E., Arke, B., Capeless, K., Cooksey, B., Steadman, A., & Gonzales, C. (2002). The effects of different types of music on perceived and physiological measures of stress. Journal of music therapy, 39(2), 101-116. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmt/39.2.101
Castelhano-Carlos, M. J., & Baumans, V. (2009). The impact of light, noise, cage cleaning and in-house transport on welfare and stress of laboratory rats. Laboratory animals, 43(4), 311-327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135543
Chikahisa, S., Sei, H., Morishima, M., Sano, A., Kitaoka, K., Nakaya, Y., & Morita, Y. (2006). Exposure to music in the perinatal period enhances learning performance and alters BDNF/TrkB signaling in mice as adults. Behavioural brain research, 169 (2), 312-319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2006.01.021
Escribano, B., Quero, I., Feijóo, M., Tasset, I., Montilla, P., & Túnez, I. (2014). Role of noise and music as anxiety modulators: Relationship with ovarian hormones in the rat. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 152, 73-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2013.12.006
Ezzone, S., Baker, C., Rosselet, R., & Terepka, E. (1998). Music as an adjunct to antiemetic therapy. In Oncology nursing forum, 25, 9, pp. 1551-1556. https://europepmc.org/article/med/9802051
Gogokhia, N., Japaridze, N., Tizabi, Y., Pataraya, L., & Zhvania, M. G. (2021). Gender differences in anxiety response to high intensity white noise in rats. Neuroscience Letters. 742, 135543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135543
Goh, R. C. W., Mu, M. D., Yung, W. H., & Ke, Y. The midline thalamic nucleus reuniens promotes compulsive-like grooming in rodents. Translational Psychiatry. 2025, 15(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-025-03283-w
Gold, C., Heldal, T. O., Dahle, T., & Wigram, T. Music therapy for schizophrenia or schizophrenia‐like illnesses. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2005, (2). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004025.pub2
Habib, O. A. A., & Sulaivany, B. S. A. Effect of Omega-3 and Multivitamins on Aluminum-Induced Changes in Serum and Tissue Enzyme Activities in Rats. Science Journal of University of Zakho. 2013, 1(1), 65-71.
Hussein, N. J. (2019). Using eye and nasal temperatures to measure positive emotions in free-range hamdani sheep. Basrah Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 31(2), 24-30. DOi:10.21276/basjas
Kalueff, A. V., & Tuohimaa, P. The grooming analysis algorithm discriminates between different levels of anxiety in rats: potential utility for neurobehavioural stress research. Journal of neuroscience methods. 2005, 143(2), 169-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2004.10.001
Knight, W. E., & Rickard, N. S. Relaxing music prevents stress-induced increases in subjective anxiety, systolic blood pressure, and heart rate in healthy males and females. Journal of music therapy. 2001, 38(4), 254-272. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmt/38.4.254
Krebs, H., Macht, M., Weyers, P., Weijers, H. G., & Janke, W. Effects of stressful noise on eating and non-eating behaviour in rats. Appetite. 1996, 26(2), 193-202. https://doi.org/10.1006/appe.1996.0015
Meshabaz, R. A., Hussein, N. J., Mersham, M. A., & Mhamed, M. S. (2017). Effect of using two music types on non-pregnant non-lactating Arabi ewes behaviour as a tool for welfare improvement. Science Journal of University of Zakho, 5(4), 301-306. https://doi.org/10.25271/2017.5.4.412
Naqvi, F., Haider, S., Batool, Z., Perveen, T., & Haleem, D. J. (2012). Sub-chronic exposure to noise affects locomotor activity and produces anxiogenic and depressive like behavior in rats. Pharmacological Reports, 64(1), 64-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1734-1140(12)70731-4
Nerweyi, N. E. H., & Al-Sulaivany, B. S. Noise pollution during the election in Duhok city/Kurdistan region of Iraq. Linguistica Antverpiensia. 2021, Issue-1pp, 677-685.
Quaranta, A., Sevi, A., Nardomarino, A., Colella, G. E., & Casamassima, D. (2002). Effects of graded noise levels on behavior, physiology and production performance of intensively managed lambs. Italian Journal of Animal Science, 1(3), 217-227. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2002.217
Rojas-Carvajal, M., Leandro, R., & Brenes, J. C. Distinct acute stressors exert an antagonistic effect on complex grooming during novelty habituation in rats. Behavioural Processes. 2023, 212, 104931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2023.104931
Rossi, E., Marrosu, F., & Saba, L. Music therapy as a complementary treatment in patients with dementia associated to Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2024, 98(1), 33-51. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-230852
Russo, C., Patanè, M., Pellitteri, R., Stanzani, S., & Russo, A. (2021). Prenatal music exposure influences weight, ghrelin expression, and morphology of rat hypothalamic neuron cultures. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 81(2), 151-158. https://doi.org/10.1002/jdn.10084
Sevi, A., Taibi, L., Albenzio, M., Muscio, A., Dell'Aquila, S., & Napolitano, F. (2001). Behavioral, adrenal, immune, and productive responses of lactating ewes to regrouping and relocation. Journal of Animal Science, 79(6), 1457-1465. https://doi.org/10.2527/2001.7961457x
Siedliecki, S. L., & Good, M. Effect of music on power, pain, depression and disability. Journal of advanced nursing. 2006, 54(5), 553-562. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.03860.x
Sung, H. C., & Chang, A. M. Use of preferred music to decrease agitated behaviours in older people with dementia: a review of the literature. Journal of clinical nursing. 2005, 14(9), 1133-1140. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2005.01218.x
Sutoo, D. E., & Akiyama, K. Music improves dopaminergic neurotransmission: demonstration based on the effect of music on blood pressure regulation. Brain research. 2004, 1016(2), 255-262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2004.05.018
Taheri, F., Joushi, S., Mohammadipoor‐Ghasemabad, L., Rad, I., Esmaeilpour, K., & Sheibani, V. Effects of music on cognitive behavioural impairments in both sex of adult rats exposed prenatally to valproic acid. Birth Defects Research. 2024, 116(1), e2300. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdr2.2300
van Erp, A. M., Kruk, M. R., Meelis, W., & Willekens-Bramer, D. C. (1994). Effect of environmental stressors on time course, variability and form of self-grooming in the rat: handling, social contact, defeat, novelty, restraint and fur moistening. Behavioural brain research, 65(1), 47-55.
Voipio, H. M. How do rats react to sound?. Scandinavian Journal of Laboratory Animal Science. Supplement (Denmark). 1997, 24(1).
Wilson, M. E., Phillips, C. J. C., Lisle, A. T., Anderson, S. T., Bryden, W. L., & Cawdell-Smith, A. J. (2011). Effect of music on the behavioural and physiological responses of stabled weanlings. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science, 31(5-6), 321-322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jevs.2011.03.157
Zhvania, M., Gogokhia, N., Tizabi, Y., Japaridze, N., Pochkidze, N., Lomidze, N., Fuad, R., & Gasimov, E. Behavioural and neuroanatomical effects on exposure to White noise in rats. Neuroscience Letters. 2020, 728, 134898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134898
Authors
Copyright (c) 2026 Nizar J. Hussein, Ronak A. Meshabaz, Aqsa Sarwar, Rukayat A. Oyegoke, Fatah M. Khalaf, Rekesh S. Habib, Nawroz A. Kakarash, Samara Saad Faraj, and Samia Mohsen El-Mahdy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License [CC BY-NC-SA 4.0] that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work, with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online.