Load Balancing and Thermal-Aware in Geo-Distributed Cloud Data Centers Based on Vlans
Abstract
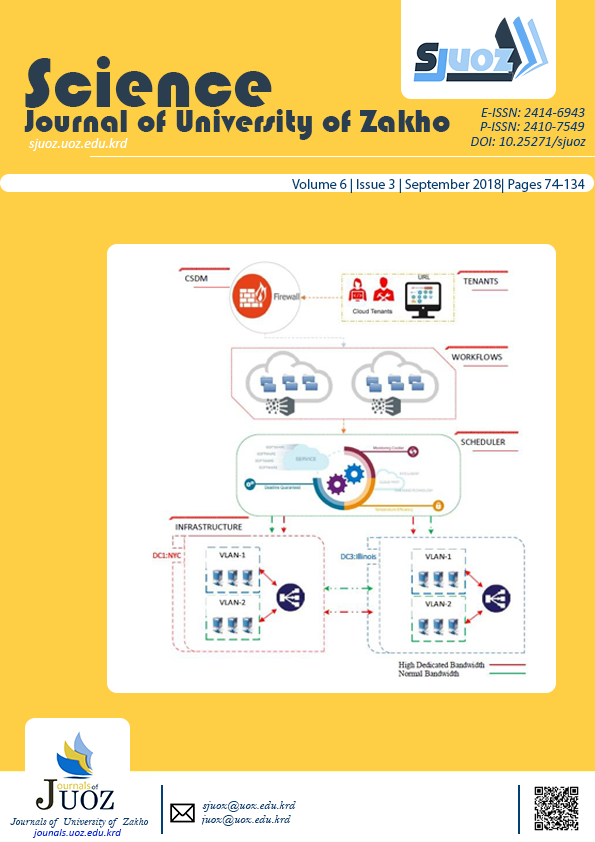
Power consumption in datacenters has become an emerging concern for the cloud providers. This poses enormous challenges for the programmers to motivate new paradigms to enhance the efficiency of cloud resources through designing innovative energy-aware algorithms. However, balancing the weights over geographically dispersed datacenters has been shown to be essential in decreasing the temperature consumption per datacenter. In this paper, we have formulated a load balancing paradigm to exploit the idea of scheduling scientific workflows over distributed cloud resources to make system outcome more efficient. The proposed heuristic works based on three constraints. First, initiating cloud resource locality for tenants and calculating the shortest distance in order to direct module applications to the closet resources and conserving more bandwidth cost. Second, selecting the most temperature aware datacenters based on geographical climate to maintain electricity cost for the providers. Third, running multiple datacenters within the same geographical location instead of housing the entire workloads in a single datacenter. This allows providers to take a tremendous advantage of sustaining the system from degradation or even unpredictable failure which in turn will frustrate the tenants. Furthermore, applications are formulated as Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)-structured workflow. For the underlying cloud hardware, our model groups the cloud servers to communicate as if they were in the same physical location. Additionally, both modes, on-demand and reservation, are supported in our algorithm. Finally, the simulation showed that our method was able to enhance the utilization rates about 67% compared to the baseline model.
Full text article
References
Authors
Copyright (c) 2018 Mustafa I. Khaleel

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License [CC BY-NC-SA 4.0] that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work, with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online.