SOLVOTHERMAL SYNTHESIS OF HIGHLY LUMINESCENT GRAPHENE QUANTUM DOTS FROM GRAPHENE OXIDE FOR DUAL APPLICATIONS IN COPPER ION SENSING AND NANOTHERMOMETRY
Abstract
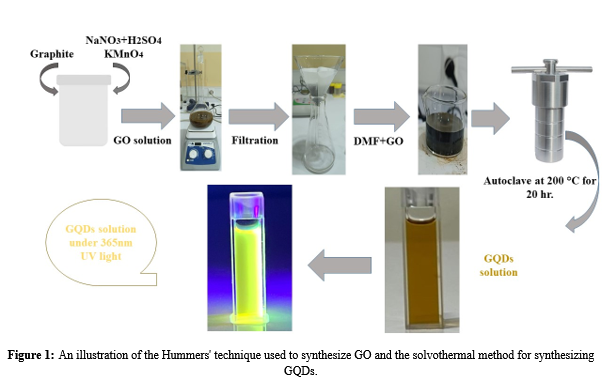
This research effectively produced graphene quantum dots (GQDs) utilizing a solvothermal method from graphene oxide (GO) with N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as the solvent. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) analyses revealed that the produced GQDs primarily exhibited a spherical morphology, with uniformly distributed nanoparticles and a mean diameter of 4.12 nm. Photoluminescence (PL) studies show excitation-dependent green emission characteristics, with an emission wavelength of 551 nm under 500 nm excitation. This is associated with a high PL intensity and a quantum yield (QY) of 51.56%. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results confirmed that the GQDs have a graphitic structure. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) confirmed the presence of oxygen functional groups, with carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen as the primary elemental components, verifying the nitrogen doping of the GQDs. The absence of other metals shows that the synthesized GQDs have a high level of purity. The synthesized GQDs were successfully utilized as an ion sensor for detecting Cu2+ ions, highlighting their exceptional sensitivity and selectivity with a limit of detection of 0.55 µm. The GQDs also exhibit potential nanothermometric behavior, as they display a photoluminescence response that depends on temperature with a sensitivity of 1.81% °C-1 between 20 °C and 70 °C. By combining nitrogen doping with a simple solvothermal synthesis, this research produces dual-function GQDs that enable both highly sensitive detection of Cu2+ ions and reliable temperature sensing.
Full text article
References
Ahirwar, S., Mallick, S., & Bahadur, D. J. A. o. (2017). Electrochemical method to prepare graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide quantum dots. ACS Omega, 2(11), 8343-8353. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b01539
Allahbakhsh, A., & Bahramian, A. R. J. J. o. M. L. (2018). Self-assembly of graphene quantum dots into hydrogels and cryogels: Dynamic light scattering, UV–Vis spectroscopy and structural investigations. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 265, 172-180. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.05.123
Bayat, A., & Saievar-Iranizad, E. J. J. o. L. (2017). Synthesis of green-photoluminescent single layer graphene quantum dots: Determination of HOMO and LUMO energy states. Journal of Luminescence, 192, 180-183. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.06.055
Carrera, C., Galán-González, A., Maser, W. K., & Benito, A. M. J. C. S. (2025). Multifaceted role of H 2 O 2 in the solvothermal synthesis of green-emitting nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. ChemicalScience. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC07896A
Chen, J., Yao, B., Li, C., & Shi, G. J. C. (2013). An improved Hummers method for eco-friendly synthesis of graphene oxide. Carbon, 64, 225-229. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.07.055
Chua, C. K., Sofer, Z., Simek, P., Jankovsky, O., Klimova, K., Bakardjieva, S.,…Pumera, M. J. A. N. (2015). Synthesis of strongly fluorescent graphene quantum dots by cage-opening buckminsterfullerene. ACS Nano, 9(3), 2548-2555. https://doi.org/https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/nn505639q
Dong, Y., Chen, C., Zheng, X., Gao, L., Cui, Z., Yang, H.,…Li, C. M. J. J. o. M. C. (2012). One-step and high yield simultaneous preparation of single-and multi-layer graphene quantum dots from CX-72 carbon black. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22(18), 8764-8766. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM30658A
Fan, C., Yang, R., Huang, Y., Mao, L., Yang, Y., Gong, L.,…Zhong, L. J. J. o. E. C. (2023). Graphene quantum dots as sulfiphilic and lithiophilic mediator toward high stability and durable life lithium-sulfur batteries. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 85, 254-266. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2023.06.030
Fan, Z., Li, S., Yuan, F., & Fan, L. J. R. A. (2015). Fluorescent graphene quantum dots for biosensing and bioimaging. RSC Advances, 5(25), 19773-19789. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA17131D
Fu, H., Ji, Z., Chen, X., Cheng, A., Liu, S., Gong, P.,…chemistry, b. (2017). A versatile ratiometric nanosensing approach for sensitive and accurate detection of Hg 2+ and biological thiols based on new fluorescent carbon quantum dots. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 409, 2373-2382. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0183-3
Gao, B., Chen, D., Gu, B., Wang, T., Wang, Z., Yang, Y.,…Wang, G. J. C. A. P. (2020). Facile and highly effective synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing probe for Cu2+ detection. 20(4), 538-544. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2020.01.018
Harde, M. T., Lakade, S., Patokar, S., More, M. P., Joshi, S., Lodha, S.,…Nangare, S. J. J. o. F. (2025). Green-Synthesized Hyaluronic Acid-Conjugated Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots for Bioimaging and Cancer Theranostics: Synthesis, Characterization, and Cytotoxicity Assessment. Journal of Fluorescence, 1-14. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-025-04388-7
Hasan, M. T., Gonzalez-Rodriguez, R., Ryan, C., Pota, K., Green, K., Coffer, J. L., & Naumov, A. V. J. N. R. (2019). Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots: Optical properties modification and photovoltaic applications. Nano Research, 12, 1041-1047. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2337-4.
Hsieh, C.-T., Sung, P.-Y., Gandomi, Y. A., Khoo, K. S., & Chang, J.-K. J. C. (2023). Microwave synthesis of boron-and nitrogen-codoped graphene quantum dots and their detection to pesticides and metal ions. Chemosphere, 318, 137926. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137926
Ifrah, Z., Shah Rukh, A., Muhammad Nauman, S., Maryam, S., & Rahat, U. J. F. i. M. (2022). Fluorescence quenching of graphene quantum dots by chloride ions: A potential optical biosensor for cystic fibrosis. Frontiers in Materials, 9, 857432. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2022.857432
Iqbal, A., Tian, Y., Wang, X., Gong, D., Guo, Y., Iqbal, K.,…Chemical, A. B. (2016). Carbon dots prepared by solid state method via citric acid and 1, 10-phenanthroline for selective and sensing detection of Fe2+ and Fe3+. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 237, 408-415. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1016/j.snb.2016.06.126
Jiang, D., Chen, Y., Li, N., Li, W., Wang, Z., Zhu, J.,…Xu, S. J. P. O. (2015). Synthesis of luminescent graphene quantum dots with high quantum yield and their toxicity study. PLOS one, 10(12), e0144906. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144906
Jin, X.-J., Tan, L., Zhao, Z.-Q., Li, M.-C., Zhou, Q.-Y., Zhang, J.-J., Zeng, Z. J. N. J. o. C. (2023). Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots with red emission and high quantum yield. New Journal of Chemistry, 47(5), 2221-2229. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1039/D2NJ04491A
Jin, Z., Owour, P., Lei, S., Ge, L. J. C. O. i. C., & Science, I. (2015). Graphene, graphene quantum dots and their applications in optoelectronics. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 20(5-6), 439-453. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2015.11.007
Kharangarh, P. R., Ravindra, N. M., Singh, G., & Umapathy, S. J. E. S. (2023). Synthesis of luminescent graphene quantum dots from biomass waste materials for energy‐related applications—an Overview. Energy Storage, 5(3), e390. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/est2.390
Kharangarh, P. R., Singh, G. J. E. J. o. S. S. S., & Technology. (2023). Effect of Mo-doped strontium cobaltite on graphene nanosheets for creating a superior electrode in supercapacitor applications. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 12(3), 031006. https://doi.org/DOI 10.1149/2162-8777/acc095
Krishnan, S. K., Singh, E., Singh, P., Meyyappan, M., & Nalwa, H. S. J. R. a. (2019). A review on graphene-based nanocomposites for electrochemical and fluorescent biosensors. RSC Advances, 9(16), 8778-8881. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA09577A
Kurniawan, D., Anjali, B. A., Setiawan, O., Ostrikov, K. K., Chung, Y. G., Chiang, W.-H. J. A. A. M., & Interfaces. (2021). Microplasma band structure engineering in graphene quantum dots for sensitive and wide-range pH sensing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 14(1), 1670-1683. https://doi.org/https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.1c18440
Lee, B. H., McKinney, R. L., Hasan, M. T., & Naumov, A. V. J. M. (2021). Graphene quantum dots as intracellular imaging-based temperature sensors. Materials, 14(3), 616. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030616
Li, X., Rui, M., Song, J., Shen, Z., & Zeng, H. J. A. F. M. (2015). Carbon and graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic and energy devices: a review. Advanced Functional Materials, 25(31), 4929-4947. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201501250
Lin, L., & Zhang, S. J. C. c. (2012). Creating high yield water soluble luminescent graphene quantum dots via exfoliating and disintegrating carbon nanotubes and graphite flakes. Chemical Communications, 48(82), 10177-10179. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC35559K
Mahato, P. K., Choudhuri, S., Kumar, C., Roy, S., & Patra, P. J. M. T. P. (2023). Evaluation of crystal size present in graphene oxide quantum dots using optical and Raman spectroscopy. materialstoday: PROCEEDINGS, 80, 668-673. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.11.066
Martins, G., Galvan, A. L. S., Valenga, M. G., Cardozo Martins, T. A., Bergamini, M. F., & Marcolino-Junior, L. H. J. A. A. N. M. (2025). Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots (N-GQDs): A Promising Material for the Development of Electrochemical Immunosensors. ACS Applied Nano Materials. https://doi.org/https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsanm.4c06568
Mohagheghpour, E., Farzin, L., & Sadjadi, S. J. B. T. E. R. (2024). Alendronate-functionalized graphene quantum dots as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for arsenic Ion detection. Biological Trace Element Research, 202(5), 2391-2401. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03819-5
Naksen, P., Khamlam, P., Khemthong, P., Yodsin, N., Phanthasri, J., Youngjan, S.,…Samphao, A. J. M. J. (2025). Nitrogen and sulfur doped graphene quantum dots as a fluorometric paper-based sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of mercury ions in aqueous samples. Microchemical Journal, 114623. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2025.114623
Novoselov, K. S., Geim, A. K., Morozov, S. V., Jiang, D.-e., Zhang, Y., Dubonos, S. V.,…Firsov, A. A. J. s. (2004). Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Sceince, 306(5696), 666-669. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1102896
Pai, A. R., Sasi, B. S., Arya, J., & Arjun, K. (2022). Synthesis of Graphene Quantum dots from the fresh leaves extract of Cynodon Dactylon and its Photoluminescence studies. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, doi:10.1088/1757-899X/1219/1/012005
Pan, D., Zhang, J., Li, Z., & Wu, M. J. A. m. (2010a). Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue‐luminescent graphene quantum dots. ADVANCED MATERIALS, 22(6), 734-738. https://doi.org/DOI: 10.1002/adma.200902825
Pan, D., Zhang, J., Li, Z., & Wu, M. J. A. m. (2010b). Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue‐luminescent graphene quantum dots. ADVANCED MATERIALS, 22(6), 734-738. https://doi.org/DOI: 10.1002/adma.200902825
Qi, B.-P., Zhang, X., Shang, B.-B., Xiang, D., & Zhang, S. J. J. o. N. R. (2018). Solvothermal tuning of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots: from preparation to photoluminescence mechanism. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 20, 1-9. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4123-8
Qu, D., Zheng, M., Du, P., Zhou, Y., Zhang, L., Li, D.,…Sun, Z. J. N. (2013). Highly luminescent S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nanoscale, 5(24), 12272-12277. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR04402E
Rajender, G., Choudhury, B., & Giri, P. J. N. (2017). In situ decoration of plasmonic Au nanoparticles on graphene quantum dots-graphitic carbon nitride hybrid and evaluation of its visible light photocatalytic performance. Nanotechnology, 28(39), 395703. https://doi.org/DOI 10.1088/1361-6528/aa810a
Reghunath, B. S., Rajasekaran, S., KR, S. D., Pinheiro, D., & UC, J. R. J. J. I. J. o. H. E. (2023). N-doped graphene quantum dots incorporated cobalt ferrite/graphitic carbon nitride ternary composite for electrochemical overall water splitting. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 48(8), 2906-2919. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.10.169
Rodwihok, C., Tam, T. V., Choi, W. M., Suwannakaew, M., Woo, S. W., Wongratanaphisan, D., & Kim, H. S. J. N. (2022). Preparation and characterization of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots from watermelon rind waste for the detection of ferric ions and cellular bio-imaging applications. Nanomaterials, 12(4), 702. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040702
Saber, Y. A., Hamed, M., Emara, S., Mansour, F. R., Locatelli, M., & Ibrahim, N. J. H. (2024). Garlic peel-based carbon quantum dots as a sustainable alternative for the sensitive and green spectrofluorometric quantification of molnupiravir in pharmaceutical capsules. Heliyon, 10(23). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40661
Salih Ajaj, C., Sadiq, D. J. N., & Nanotechnology. (2023). Mulberry Juice‐Derived Carbon Quantum Dots as a Cu2+ Ion Sensor: Investigating the Influence of Fruit Ripeness on the Optical Properties. Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, 2023(1), 9980479. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/9980479
Sehrawat, P., & Islam, S. J. N. A. (2019). An ultrafast quantum thermometer from graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale
Advances, 1(5), 1772-1783. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NA00361K
Authors
Copyright (c) 2026 Sitya Hishyar Ali and Diyar Sadiq

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License [CC BY-NC-SA 4.0] that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work, with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online.